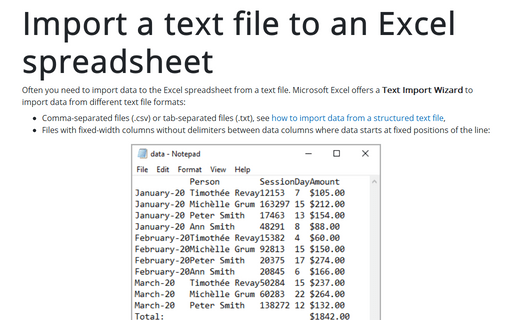
Import a text file to an Excel spreadsheet
- Comma-separated files (.csv) or tab-separated files (.txt), see how to import data from a structured text file,
- Files with fixed-width columns without delimiters between data columns where data starts at fixed positions of the line:
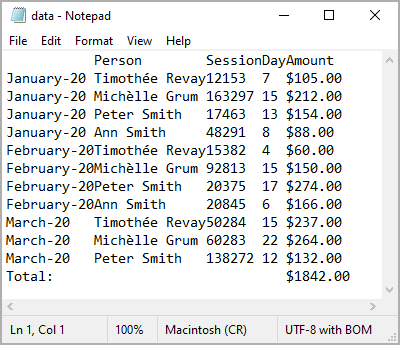
To import data from a text file, do the following:
1. On the File tab, click Open (or click Ctrl+O).
2. On the Open pane, click the Browse button:
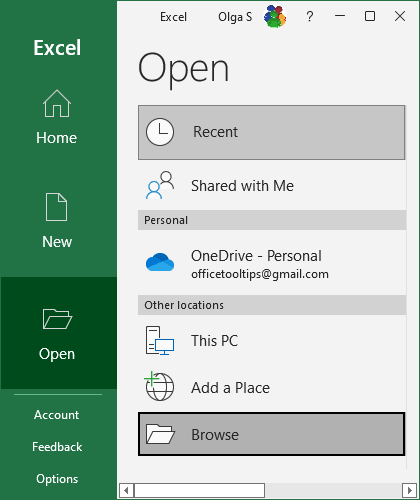
3. On the Open dialog box:
- Select the path to the text file you want to import,
- From the File Type dropdown list, select All Files or Text Files:

- Click the Open button.
4. In the Text Import Wizard – Step 1 of 3 dialog box:
4.1. In the Original data type group, choose the Fixed width option:
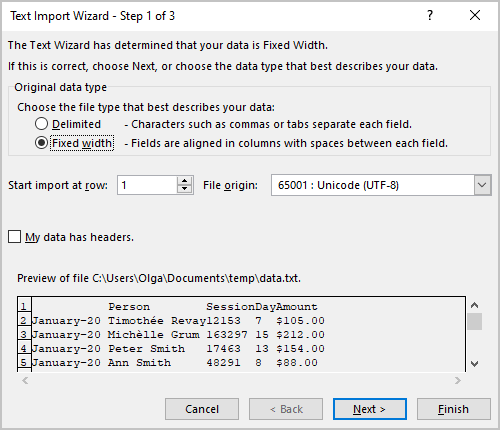
Note: If you see delimiters, leave the option Delimited selected and follow the steps of importing a structured text file.
4.2. You can change the File origin to use another encoding to display the data (you need to know the character encoding for the data or try other encodings until you see the correct data in the preview section):
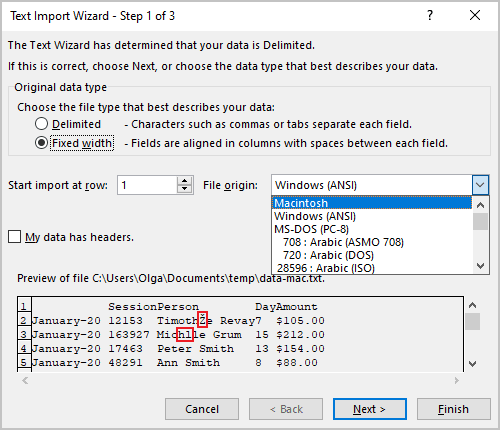
4.3. Click the Next > button.
5. In the Text Import Wizard – Step 2 of 3 dialog box:
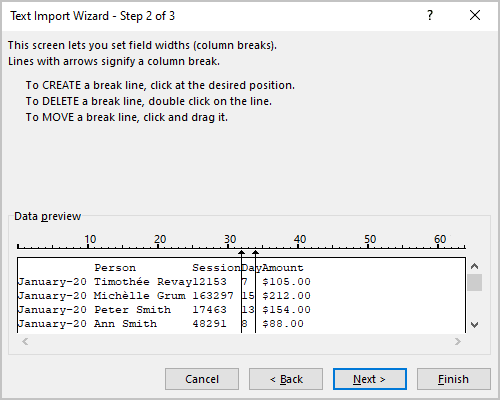
5.1. Create, move, and delete break lines:
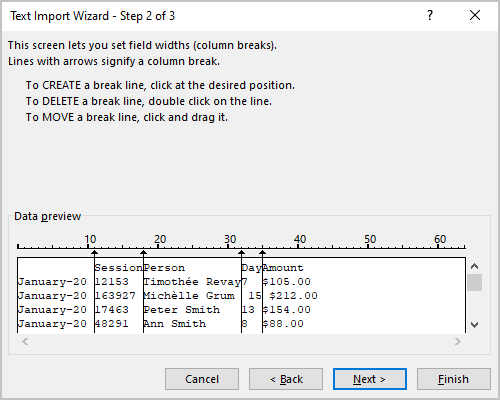
5.2. Click the Next > button.
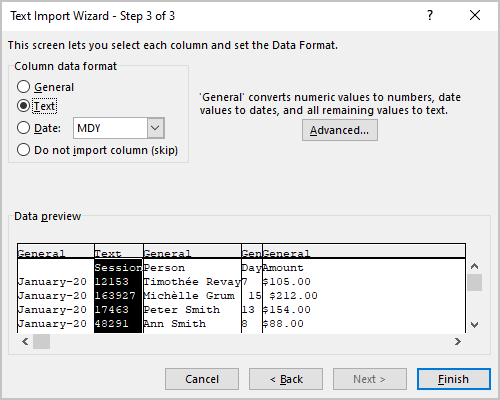
6. In the Text Import Wizard – Step 3 of 3 dialog box:
6.1. Select the column and the appropriate data format for this column in the Column data format group:
Notes:
- You can skip this step and format columns after importing.
- You can click the Advanced... button to select the correct Decimal separator and Thousands separator (see how to change the used by default decimal symbol and digit grouping symbol):

- You can ignore some columns for importing by selecting the Do not import column (skip) in the Column data format group (the second column Session in the previous example).
6.2. Repeat the previous step for all columns you want to import and click Finish.
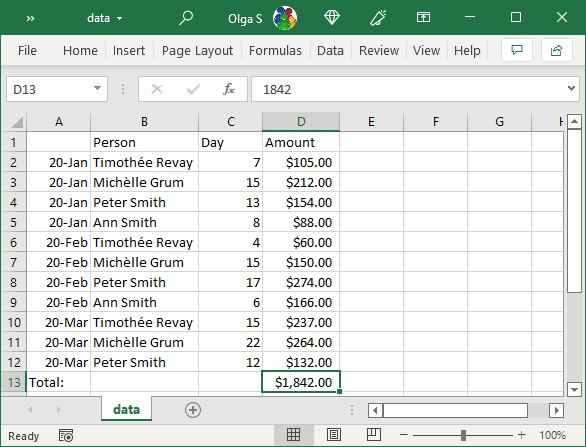
Excel imports all the data you selected:
See also this tip in French: Comment importer un fichier texte dans la feuille de calcul Excel.