Design a table in Word
Usually, the table contains the following basic components:
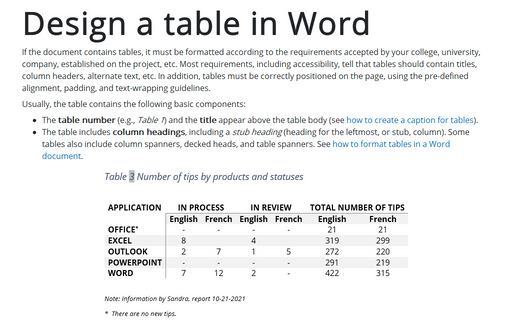
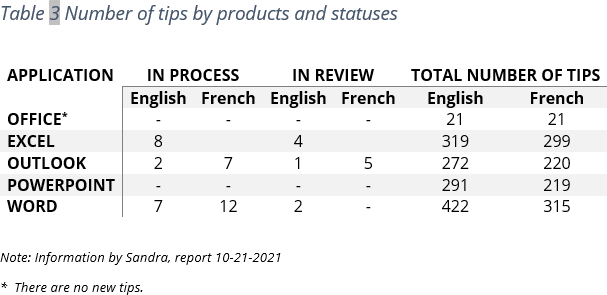
- The table number (e.g., Table 1) and the title appear above the table body (see how to create a caption for tables).
- The table includes column headings, including a stub heading (heading for the leftmost, or stub, column). Some tables also include column spanners, decked heads, and table spanners. See how to format tables in a Word document.
- The table body contains all the rows and columns of a table (including the headings row). A cell is the point of intersection between a row and a column. See how to select and format table elements.
- All types of notes (general, specific, and probability) appear below the table if there are notes. Notes describe contents of the table that cannot be understood from the table title or body alone (e.g., definitions of abbreviations, copyright attribution, etc.).
See also how to create cross-references to a table.
Align the table on the page
By default, Word aligns the table to the Left. If you want to change an alignment of the table on the page, select it and do one of the following:
- On the Home tab, in the Paragraph group, select the alignment you prefer:

- Open the Table Properties dialog box by doing one of the following:
- On the Table Layout tab, in the Table group, click the Properties button:

- Right-click the table and select Table Properties... in the popup menu:

In the Table Properties dialog box, on the Table tab, in the Alignment section, select the option you prefer:

- On the Table Layout tab, in the Table group, click the Properties button:
- Press the keyboard shortcuts:
- Ctrl+L to align a table to the Left (by default),
- Ctrl+E to Center the table,
- Ctrl+R to align a table to the Right.
Add indent from left
The Indent from left controls the distance of the table from the left margin. To add the Indent from left, do one of the following:
- On the Home tab, in the Paragraph group, click the Increase Indent button:
- Open the Properties dialog box. In the Table Properties dialog box, on the Table tab, in the Alignment section, type or choose the value you need in the Indent from left field:

Note: The Indent from left field is active only for the Left alignment.
For example, the table with a left indent 0.5 inches:

Text Wrapping for a table
Word offers to customize the text wrapping style for a table, as well as for figures. To customize a text wrapping style, do the following:
1. Select a table.
2. Open the Table Properties dialog box. In the Table Properties dialog box, on the Table tab, in the Text wrapping section:
- Select None to disable text wrapping for the table
- Select the Around option to have text wrapping around the table. Then click the Positioning... button for more customization:

In the Table Positioning dialog box:

Position a table
- In the Horizontal sections, specify:
- Position to the Left, Right, Center, Inside, or Outside,
- Relative to the Margin, Page, or Column.
For example, with Position to the Right relative to Margin:

- In the Vertical section, specify:
- Position to the Top, Bottom, Center, Inside, or Outside,
- Relative to the Margin, Page, or Column.
For example, with Position to the Top relative to Page:

Increase the space between text and table
- In the Distance from surrounding text section, enter custom values for the distance between the text and the table independently for:
- Top (0 by default),
- Bottom (0 by default),
- Left (1.13 inches by default),
- Right (1.13 inches by default).
For example, with the 0.3-inch distance on all sides:

Note: See also how to change a distance within a table.
Text wrapping options
- In the Options section:
- The Move with text option moves the table along with the text in which it is located.
Select the Move with Text option if the text is directly related to the table data. The table is vertically aligned to the related paragraph around it. If the table data applies to the whole document, keep the Move with Text option unselected.
- Allow overlap allows to layer table on top of each other.
- The Move with text option moves the table along with the text in which it is located.
Position a large table
If the table is too long for one page, or when a table needs to be placed at the bottom of the page, Word splits it between pages. See How to keep a row of the table on one page in a Word document and How to keep a table on one page of a Word document. Also, most requirements recommend duplicating column headers for every table part.
If the table is too wide to fit on one page, it is necessary to use landscape orientation on the page with the wide table.
Control where a table is split
When working with a long table, or when a table needs to be placed at the bottom of the page, splitting up a table into two separate tables is necessary. By default, if a page break occurs within a large row, Microsoft Word allows a page break to split the line between two pages (see How to prevent a table break between pages).
To insert a table break at a specific location, position the cursor on the cell on the row, or select the row that should appear on the next page, then do one of the following:
- Press Ctrl+Enter.
- On the Table Layout tab, in the Merge group, click the Split Table button:
Be careful! Word applies the chosen style to the new table. If you Undo the table splitting, the formatting may not be Undone correctly.
Add an Alternative text (Alt Text)
Most requirements recommend adding alternative text for visual objects, including tables (see how to turn off automatically creating the Alternative text).
To add an alternative text for a table, do the following:
1. Select a table.
2. Do one of the following:
- On the Table Layout tab, in the Table group, click the Properties button.
- Right-click the table and select Table Properties... in the popup menu.
3. In the Table Properties dialog box, on the Alt Text tab:
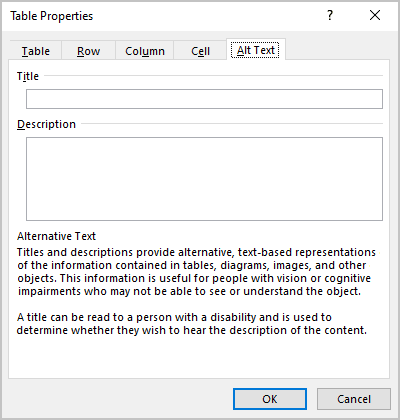
- In the Title field, type a title, if necessary.
- In the Description field, fill the description for the table.
- Click the OK button.